THE PROBLEM
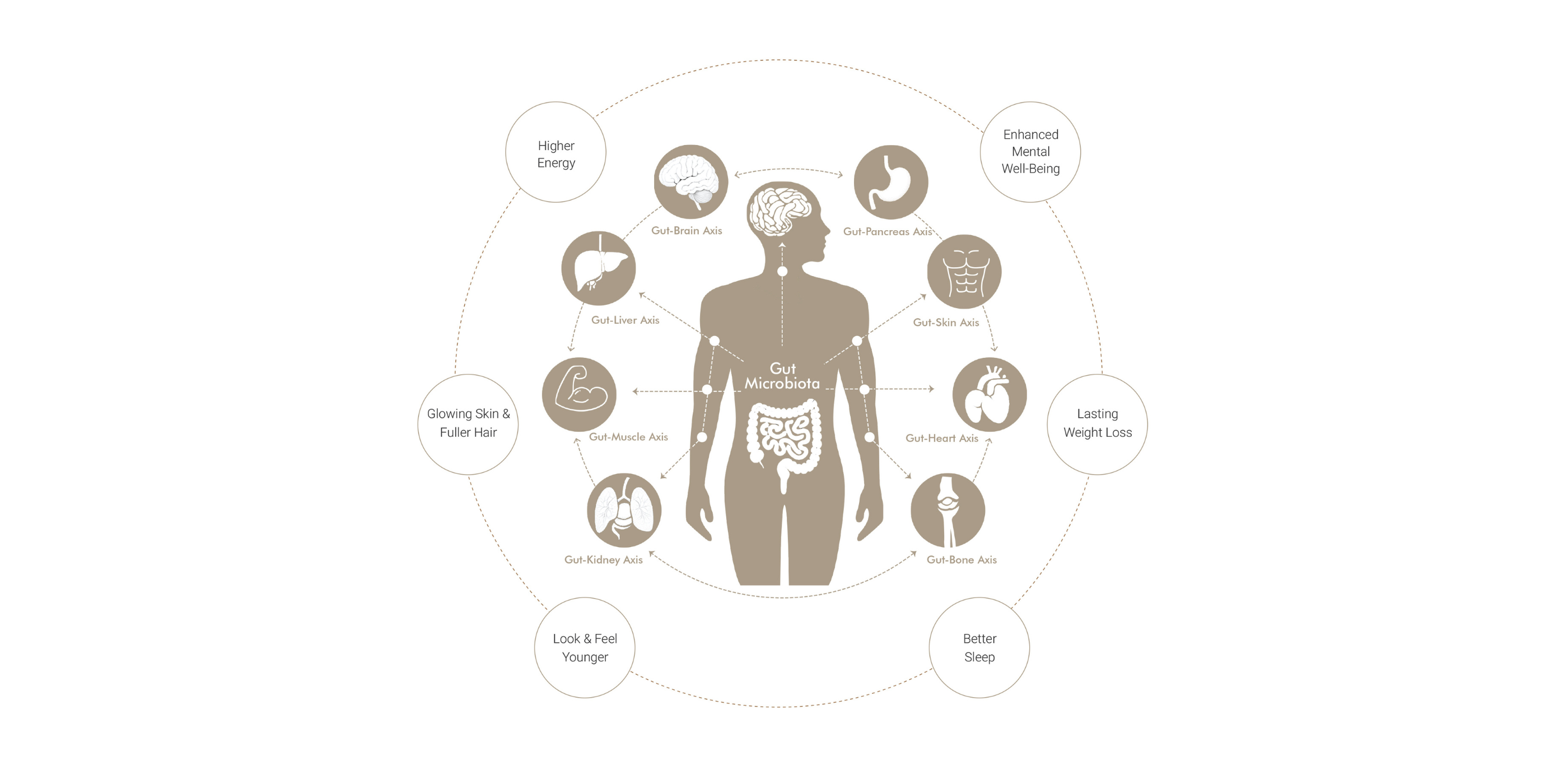
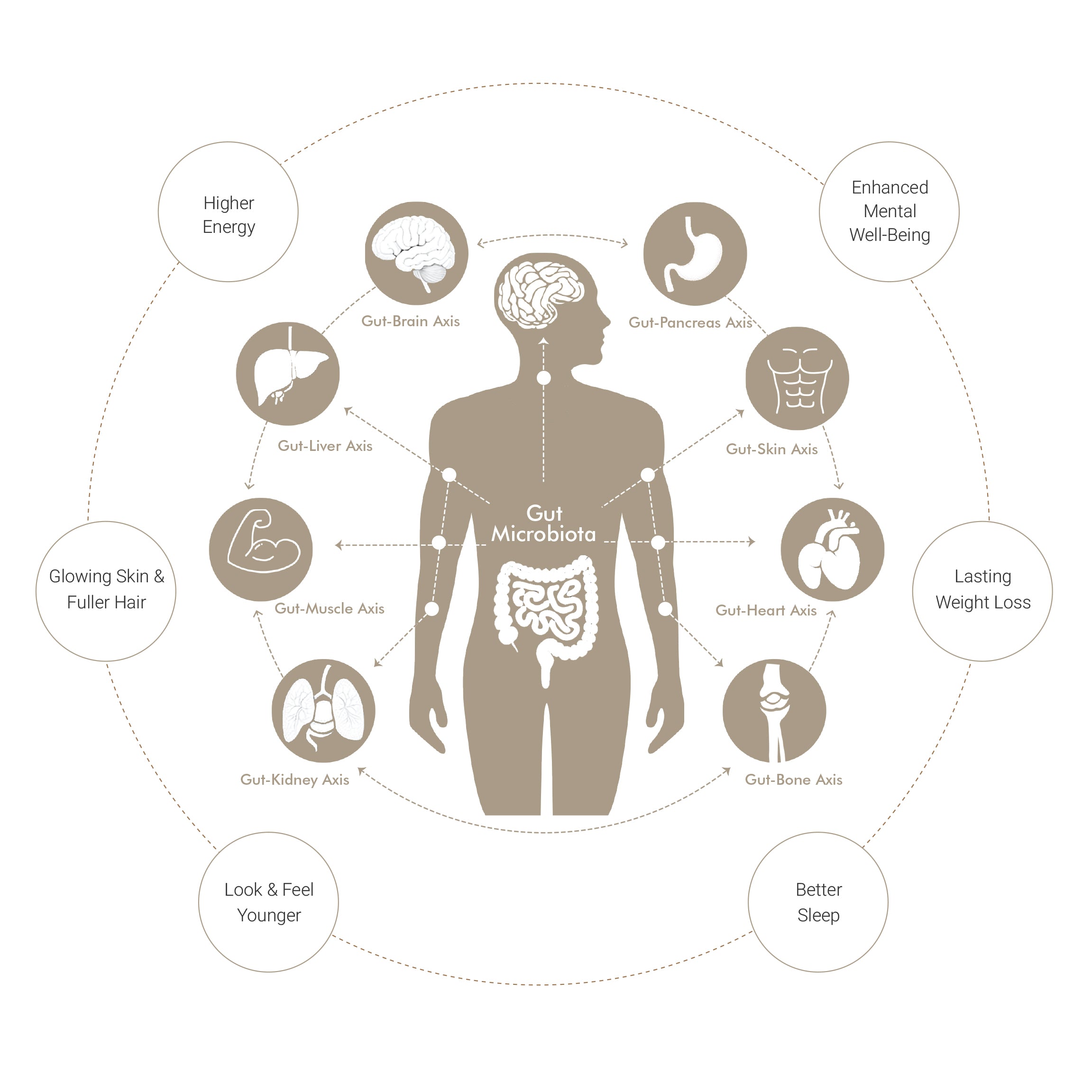
health begins in the gut
Research links gut toxins to chronic inflammation, impacting weight, health, and aging. A balanced gut microbiome supports immunity, mood, metabolism, and skin.
THE SOLUTION
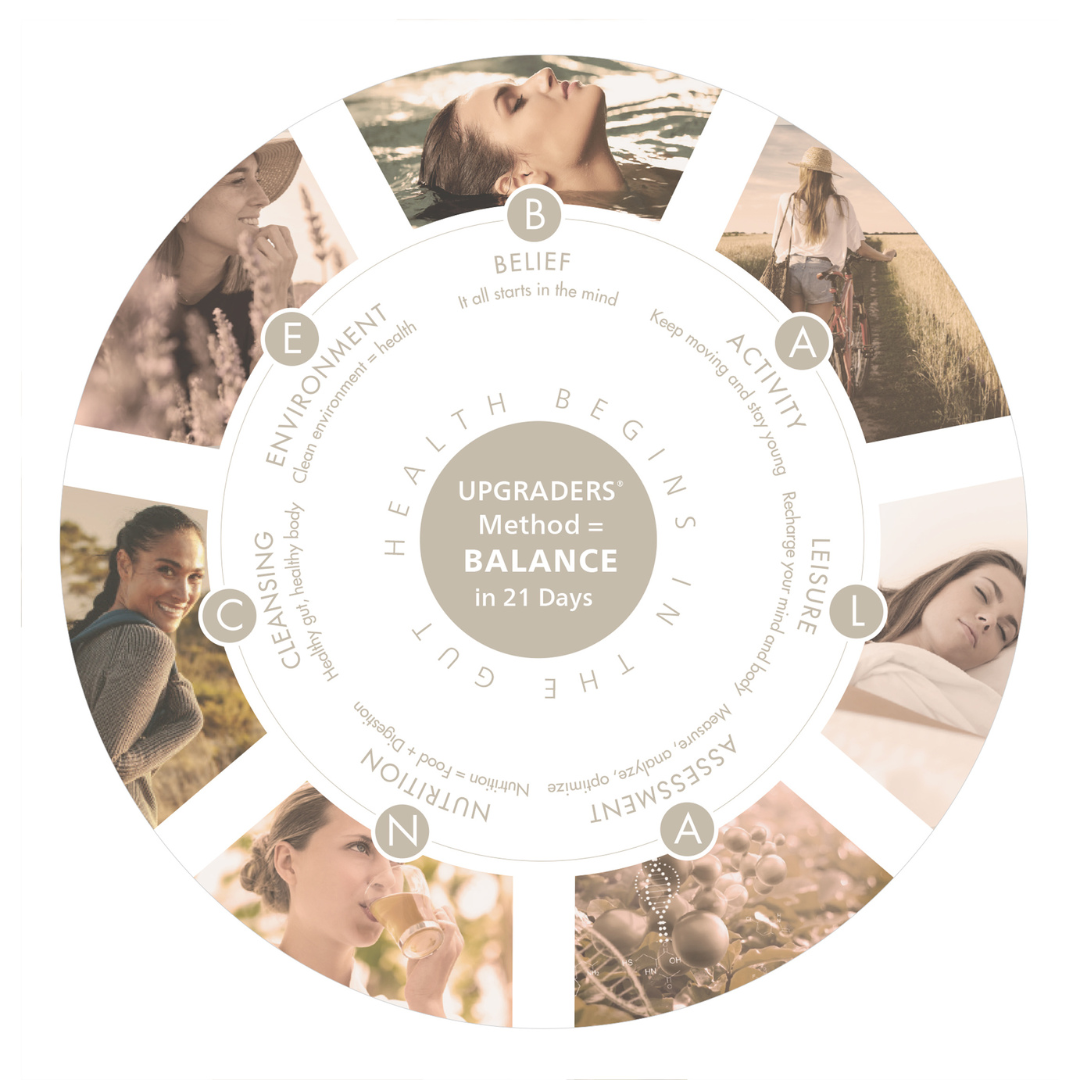
UPGRADERS® method = BALANCE
Only a body in BALANCE (equilibrium) can heal, lose weight, sleep better, look younger & thrive ...
B = BELIEF
It all starts in the mind. Optimistic people are healthier.
A = ACTIVITY
Keep moving and stay young. Physically active adults are 9 years younger.
L = LEISURE
Recharge your mind and body. Insomnia affects cognition, behavior & judgment.
A = ASSESSMENT
Track, analyze, optimize. A healthy body is in BALANCE: pH 7.0-8.0 in saliva.
N = NUTRITION
Nutrition = Food + Digestion. If “digestion” is inadequate, the body can't be nourished.
C = CLEANSING
Clean gut, healthy body. Toxins need to be eliminated for optimal health.
E = ENVIRONMENT
Clean environment = health. From air pollution to pesticides..., environmental toxins are making us sick.
REFERENCES
- Claude Bernard, founder of modern Physiology, 1813-1878, cited in „Leçon sur les auto-intoxications dans les maladies“ by Charles Bouchard 1885
- Spivak I, Fluhr L, Elinav E. Local and systemic effects of microbiome-derived metabolites. EMBO Rep. 2022 Oct 6;23(10):e55664. doi:10.15252/embr.202255664. Epub 2022 Aug 29. PMID: 36031866; PMCID: PMC9535759.
- Sagar NA, Tarafdar S, Agarwal S, Tarafdar A, Sharma S. Polyamines: Functions, Metabolism, and Role in Human Disease Management. Med Sci (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;9(2):44. doi: 10.3390/medsci9020044. PMID: 34207607; PMCID: PMC8293435.
- Nagpal R, Mainali R, Ahmadi S, Wang S, Singh R, Kavanagh K, Kitzman DW, Kushugulova A, Marotta F, Yadav H. Gut microbiome and aging: Physiological and mechanistic insights. Nutr Healthy Aging. 2018 Jun 15;4(4):267-285. doi: 10.3233/NHA-170030. PMID:29951588; PMCID: PMC6004897.
- Hughes RL, Holscher HD. Fueling Gut Microbes: A Review of the Interaction between Diet, Exercise, and the Gut Microbiota in Athletes. Adv Nutr. 2021 Dec 1;12(6):2190-2215. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab077. PMID: 34229348; PMCID: PMC8634498.
- Itoh et al., Peak blood ammonia and lactate after submaximal, maximal and supramaximal exercise in sprinters and long-distance runners.Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1990;60(4):271-6.
- Mutch et al., Ammonia metabolism in exercise and fatigue: a review., Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1983;15(1):41-50.
- Simons CC, Schouten LJ, Weijenberg MP, Goldbohm RA, van den Brandt PA. Bowel movement and constipation frequencies and the risk of colorectal cancer among men in the Netherlands Cohort Study on Diet and Cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 2010 Dec 15;172(12):1404-14. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwq307. Epub 2010 Oct 27. PMID: 20980354.
- Ma N, Tian Y, Wu Y, Ma X. Contributions of the Interaction Between Dietary Protein and Gut Microbiota to Intestinal Health. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(8):795-808. doi: 10.2174/1389203718666170216153505. PMID: 28215168.
- Zhou ZL, Jia XB, Sun MF, et al. Neuroprotection of Fasting Mimicking Diet on MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mice via Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Neurotherapeutics.2019;16(3):741-760. doi:10.1007/s13311-019-00719-2
- Hayaishi O. My life with tryptophan--never a dull moment. Protein Sci. 1993 Mar;2(3):472-5. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020320. PMID:8453383; PMCID: PMC2142392.
- Ninan J, Feldman L. Ammonia Levels and Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Known Chronic Liver Disease. J Hosp Med. 2017 Aug;12(8):659-661. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2794. PMID: 28786433.
- Niknahad H, Jamshidzadeh A, Heidari R, Zarei M, Ommati MM. Ammonia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and energy metabolism disturbances in isolated brain and liver mitochondria, and the effect of taurine administration: relevance to hepatic encephalopathy treatment. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017;3(3):141-151. doi:10.5114/ceh.2017.68833
- Bobermin LD, Souza DO, Gonçalves CA, Quincozes-Santos A. Resveratrol prevents ammonia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular redox imbalance in C6 astroglial cells. Nutr Neurosci. 2018 May;21(4):276-285. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2017.1284375. Epub 2017 Feb 6. PMID: 28165879.
- MahmoudianDehkordi S, Arnold M, Nho K, Ahmad S, Jia W, Xie G, Louie G, Kueider-Paisley A, Moseley MA, Thompson JW, St John Williams L, Tenenbaum JD, Blach C, Baillie R, Han X, Bhattacharyya S, Toledo JB, Schafferer S, Klein S, Koal T, Risacher SL,Kling MA, Motsinger-Reif A, Rotroff DM, Jack J, Hankemeier T, Bennett DA, De Jager PL, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM, Weiner MW,Doraiswamy PM, van Duijn CM, Saykin AJ, Kastenmüller G, Kaddurah-Daouk R; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative and the Alzheimer Disease Metabolomics Consortium. Altered bile acid profile associates with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease-An emerging role for gut microbiome. Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Jan;15(1):76-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.07.217. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Erratum in: Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Apr;15(4):604. PMID: 30337151; PMCID: PMC6487485.
- Itoh et al., Peak blood ammonia and lactate after submaximal, maximal and supramaximal exercise in sprinters and long-distance runners.Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1990;60(4):271-6.
- Büngeler, W.: Die experimentelle Erzeugung von Leukämie und Lymphosarkom durch chronische Indol Vergiftung der Maus. Frankfurt. Z. Path. 44 (1933), 202
- Li X, Zhang B, Hu Y, Zhao Y. New Insights Into Gut-Bacteria-Derived Indole and Its Derivatives in Intestinal and Liver Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 13;12:769501. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.769501. PMID: 34966278; PMCID: PMC8710772.
- González-Regueiro JA, Higuera-de la Tijera MF, Moreno-Alcántar R, Torre A. Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy and future treatment options. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2019 Apr-Jun;84(2):195-203. English, Spanish. doi: 10.1016/j.rgmx.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Apr 20. PMID: 31014748. – 96 – – 97
- Senthong V et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Mortality Risk in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5:e004237
- https://www.biovis-diagnostik.eu/wp-content/uploads/biovis-TMAO-DE.pdf
- Makrecka-Kuka M, Volska K, Antone U, Vilskersts R, Grinberga S, Bandere D, Liepinsh E, Dambrova M. Trimethylamine N-oxide impairs pyruvate and fatty acid oxidation in cardiac mitochondria. Toxicol Lett. 2017 Feb 5;267:32-38. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.12.017. Epub 2016 Dec 31. PMID: 28049038.
- Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association 2019 15, 76-92DOI: (10.1016/j.jalz.2018.07.217)
- Sato, Y., Atarashi, K., Plichta, D.R. et al. Novel bile acid biosynthetic pathways are enriched in the microbiome of centenarians. Nature (2021 July 29th). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03832-5
- Lamichhane S, Sen P, Dickens AM, Orešič M, Bertram HC. Gut metabolome meets microbiome: A methodological perspective to understand the relationship between host and microbe. Methods. 2018 Oct 1;149:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.04.029. Epub 2018 Apr 30. PMID: 29715508.
- Binienda A, Twardowska A, Makaro A, Salaga M. Dietary Carbohydrates and Lipids in the Pathogenesis of Leaky Gut Syndrome: An Overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 8;21(21):8368. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218368. PMID: 33171587; PMCID: PMC7664638.
- Harry Sokol et al „Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients”, PNAS 2008 105:16731-16736
- Dr. sc. med. Bodo Kuklinski. „Mitochondrien.“ iBooks 2015, ISBN EBook 978-3-89901-928-5